Deciding to hire an SEO professional is a decision that can improve your website traffic, ROI, and save time. Many SEO professionals provide useful services like a review of your site content or structure, technical advice on website development, content development, management of online campaigns, and keyword research.
First, here is a quick overview of important concepts to understand.
Index –
Google stores all the web pages that it knows about in its index. Each index entry describes the content and the location (URL) of that page. Content can include text, images, and video files. The best way to think about indexing is that it acts as a giant directory for the internet.
Crawl –
Crawling is the process of looking for new or updated pages that exist on the internet. Google starts this process by following backlinks, reading site maps, and more. Google crawls the web and looks for new pages, and then indexes them. Google completes this process using the Crawler, better known as GoogleBot, an automated software.
SEO – Search Engine Optimization.
SEO makes a website better for search engines and improves the potential for a greater ROI.
These key concepts will help in understanding the basics of how Google works. In order to index a site, there are three technical requirements to pass for a site to be eligible to be indexed by Google Search:
- GoogleBot isn’t blocked.
- Google Bot is the generate name for Google’s two types of web crawlers.
- Google downloads content, images, and videos from pages that exist on the web via crawlers.
- The page works.
- This means Google has received a success status code.
- The page has indexable content.
- Indexable content means the text content is in a file type that Google Search supports, and content doesn’t violate spam policies.
In addition, there are five key factors of a Google search query that should be addressed. To learn more about the five key factors, read on here.
Now that you know the three technical requirements and the five key factors of a google search, your business is one step closer to getting to the first page of Google.
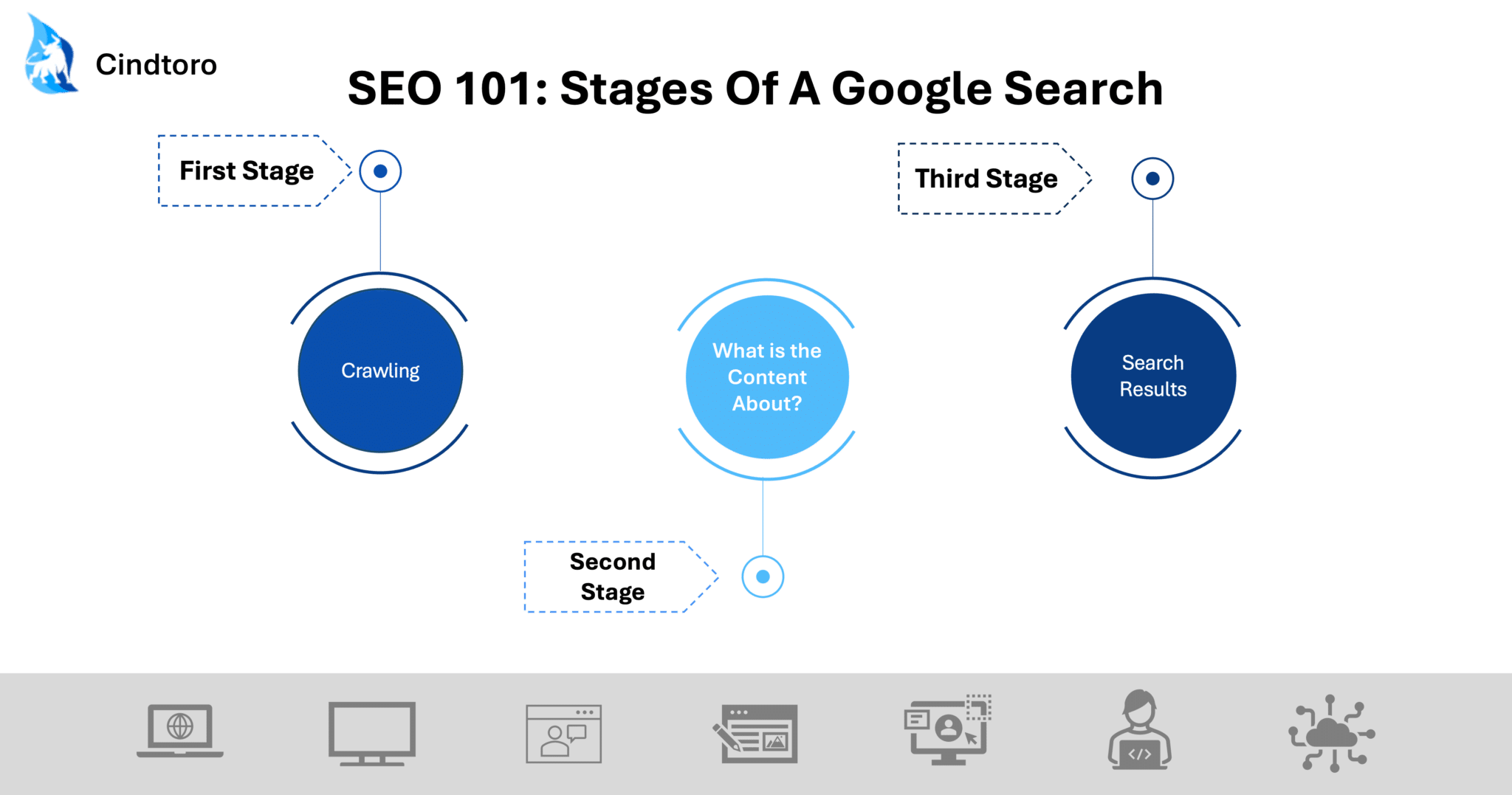
The First Stage
Google stores all the web pages that it knows about in its index. Each index entry describes the content and the location (URL) of that page. The best way to think about indexing is that it acts as a giant directory for the internet.
The first stage of Google is finding out what pages exist on the web and searches for new or updated web pages. This process is called Crawling. Google crawls the web and looks for new pages, and then indexes them.
GoogleBot can discover pages when following a link from a known page to a new page. For example, a category page links to a new blog post. Once GoogleBot discovers a page’s URL, it may visit the page to find out what’s on it. During the crawl, Google renders the page and runs Javascript. This rendering process is important because it brings content to the page so users can see it. Of course, the most important requirement to the first stage of Google, crawling, is that GoogleBot has access to a business’s website.
The Second Stage
After a page is crawled, Google tries to understand what the content is about. This is the indexing stage. This stage includes processing and analyzing text content, key content tags and attributes (such as <title> elements and alt attributes), images, and videos.
During indexing, Google determines if a page is a duplicate of another page. A duplicate page is referred to the canonical, which is the page that may be shown in search results. Google selects the canonical by clustering (or grouping) pages found on the internet that have similar content. Then, Google selects the page with the information that users need for that topic. The other pages serve as alternative versions with different information.
Google can also collect signals about the canonical page and its content, which can be used in the third stage. Collected information includes language of the page, the country the content is local to (such as US or UK), the ease of usability of the page, and more. The collected information is stored in the Google index, Google’s form of a directory.
The Third Stage
The last and final stage of a Google Search is serving search results. Search results are largely dependent relevancy for a particular user. Relevancy is determined by hundreds of factors, such as user’s location, language, and device. For example, if a user allows Google to access their location, searching “restaurant near me” will show different restaurants for a user in Florida than it would a user in California.
In addition, results can change based on different keywords a user inputs into the query. For example, searching for “furniture store” will likely show local furniture stores nearby and no images. However, searching for “modern dining room table” is more likely to show images and no local results.
That is a general overview of the three stages of a Google search. SEO professionals play an important role in helping a business navigate the complexities of Google search. SEO professionals understand these complexities and can help push your business to reach the first page of Google. They can achieve this by running advertisement campaigns, review site’s content, offer technical advice on website development, and structure effective marketing plans tailored to certain demographics. To learn more about how Cindtoro Digital Marketing can help your business gain more traffic, schedule a quick consultation.
FAQs you may have
At which stage of the process does google determine what each page is about?
After the Indexing stage is complete: Google determines what each page is about after they have had time to crawl and index a website. They use their 200+ ranking factors to understand where to place your website with in the search results pages or SERPS for short.