Introduction
Google Analytics is one of the most effective tools for digital marketers available. When used correctly it can help your marketing campaigns thrive. But if there are data issues or you do not understand certain elements about how Google Analytics collects and tracks data it will hurt your advertising efforts and skew your results. One of the most misunderstood parts of analytics is direct traffic. It is elusive, hard to track, and can make you think you are doing better than you really are.
In this article by the Cindtoro team we will review what does direct traffic mean in Google Analytics 4, help you diagnose direct traffic issues, and provide steps you can take to reduce GA4 direct traffic to manageable levels so you can stop it from wreaking havoc on your advertising efforts.
2. Understanding Direct Traffic in GA4
What Does Direct Mean in Google Analytics?
In Google Analytics, “direct” traffic refers to website visits where the source cannot be determined. This means a user did not arrive from a known source like a search engine, another website (referral traffic), or a marketing campaign.
This type of traffic happens with a few different instances: a user types the URL directly into their browser, they use a bookmark, or click a link from a source that does not pass on referral information via UTM code such as a PDF or an app.
Common Misconceptions
Most marketers and data analysts wrongfully assume that direct traffic always indicates a strong brand recognition and credibility. Most of the time a “marketer” will say these are users who type your website url into their browser because they know your brand. But we know from real world experience that this is not the case.
We learned this the hard way when we first started our company in 2019. we had an overwhelming amount of search engine traffic despite at the time never invested in any type of SEO whatsoever.
We knew something was wrong. It would have been impossible for a brand new business to get 100s of website visitors straight out the gate with no organic search presence.
Importance of Accurate Attribution
It is very simple. If you want to advertise to the correct audience and maximize your ROI you will need to dial in your Google analytics tracking. Accurate attribution is the foundation of digital marketing. Without it you will not be able to assess what is working and what is not.
3. Diagnosing Direct Traffic Issues
Diagnosing traffic issues can be done in a number of ways. In the next few paragraphs our team is going to take you down the most common ways to spot direct traffic issues.
Identifying Unusual Spikes
Identifying unusual traffic spikes is not as difficult as you may think. Most of the time a traffic spike will happen due to bot traffic. Traffic spikes are becoming increasingly common, especially with AI tools constantly crawling your website.
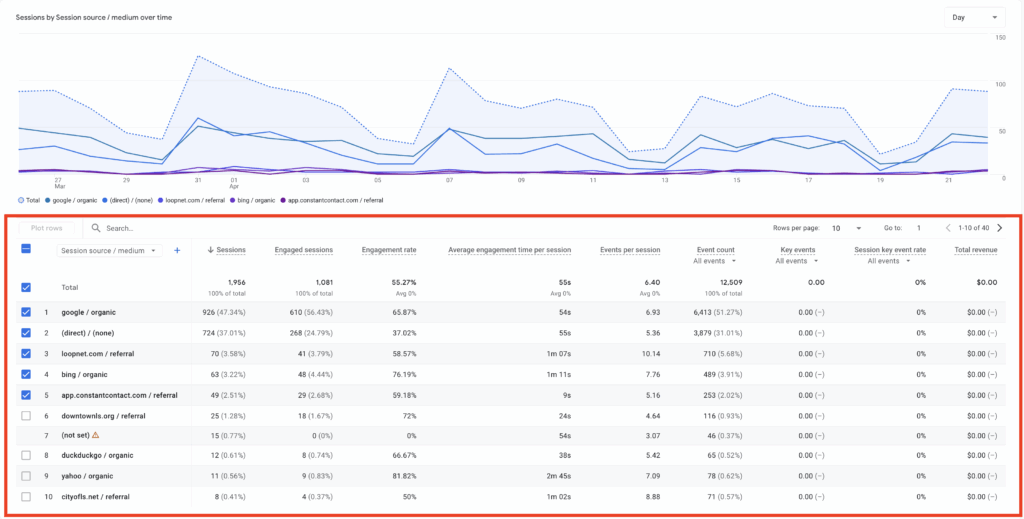
Here is what a traffic spike looks like
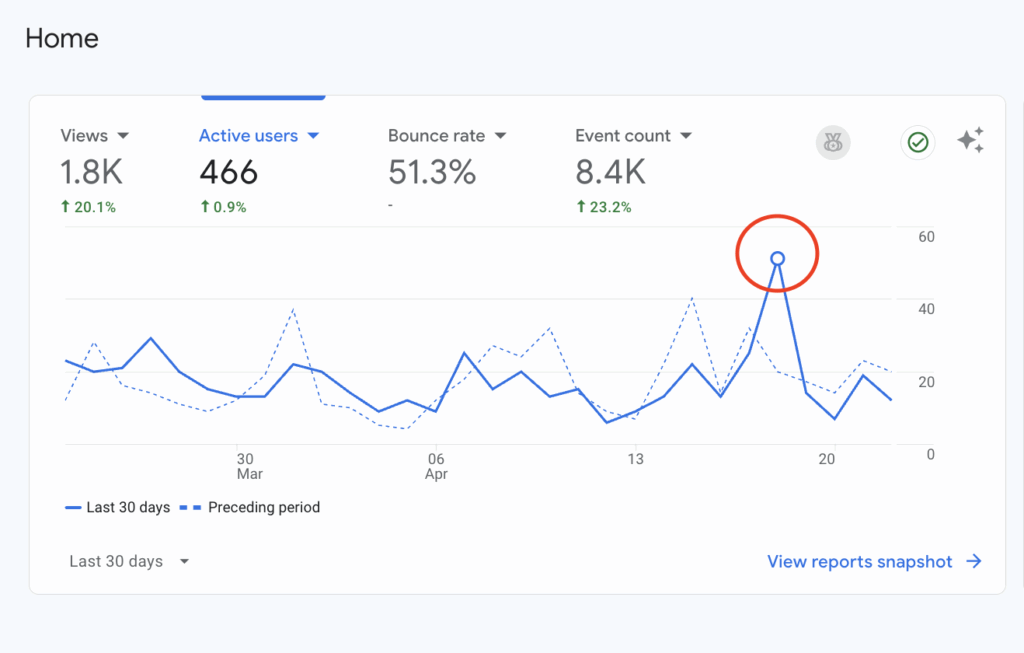
In order to find a traffic spike you will want to look for massive peaks / valleys within your Google Analytics account. If you see these things happening consistently you are likely being pinged by bots or Google web crawlers.
Analyzing Landing Pages
Every webpage on your site will drive various amounts of search engine traffic, sometimes you will have times where you will feel like your data is “off.” The easiest way to do this is to go to the “pages and screen class” report on analytics. Here you will be able to see if your data is being impacted by bot traffic or has a large amount of direct traffic coming to it. If you see something that looks abnormally high for your business you likely have direct traffic tracking issues.
Utilizing Secondary Dimensions – Steps To Locate Session medium / session source
If you do not want to use the “pages and screen class” report or the overview. You can gain additional insights into the user behavior across your website by using secondary dimensions. One of the most useful reports for this is the “session medium / session source” section of Google Analytics 4. If you are a seasoned user this will be easy to find however if you are just getting started or you do not know where to find it we have outlaid all the steps below.
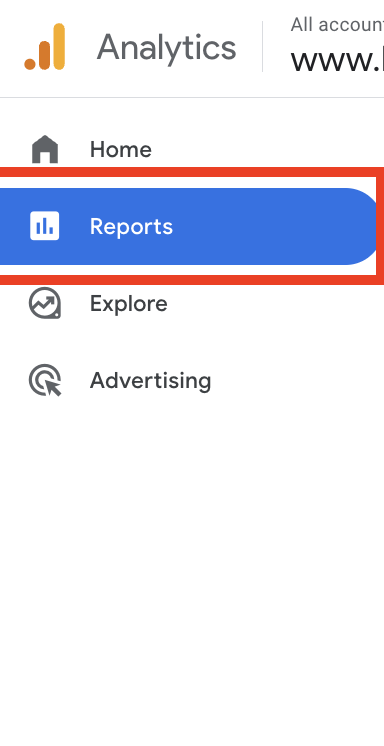
Step 1
After your have selected the correct property In the top left hand corner of your GA4 account click on “reports.”
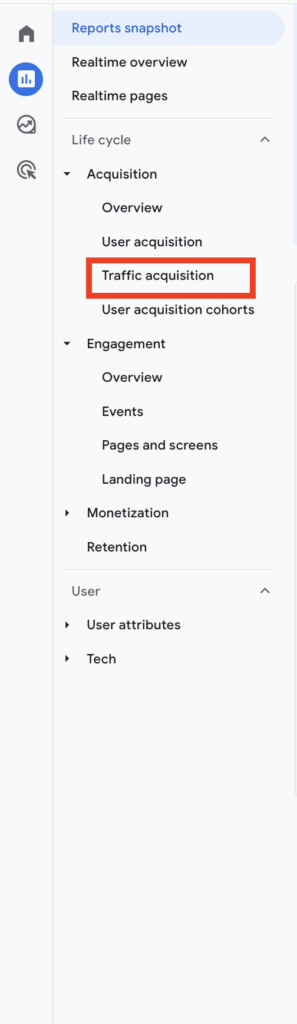
Step 2
You should see a side bar in the left hand corner with multiple options from here you should select “Traffic acquisition.”
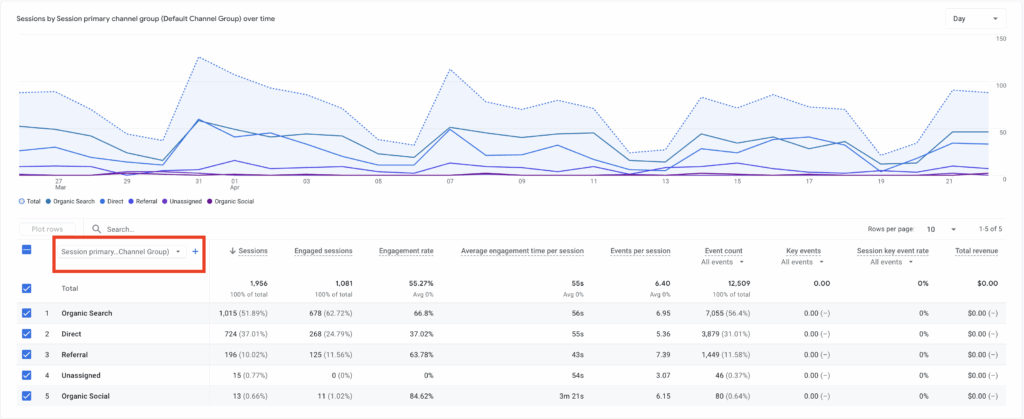
Step 3
Once you select traffic acquisition navigate to the table in the center of the screen select the dropdown “Session Primary (Channel Group)”.
Step 4
You should see a dropdown box that opens with a few options select “Session source / medium“.
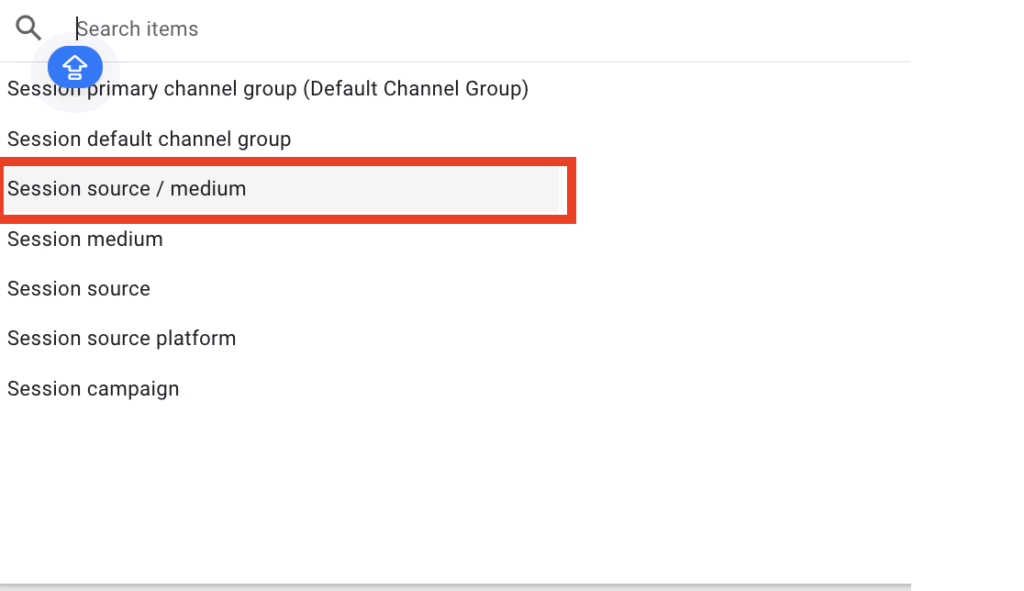
Step 5
Finally, you will know you have reached the correct place where you can see the session source AND the medium in the center table. As an example: “Google / Organic”.
4. Common Causes of Direct Traffic Misattribution
Understanding Google Analytics 4 direct traffic misattribution can be a difficult task as there are a number of things that can cause it. Below we will be discussing the four most common was direct traffic happens.
Missing or Incorrect UTM Parameters
Missing or incorrect UTM parameters are a primary reason for direct traffic in Google Analytics 4 (GA4). UTM parameters are crucial for tracking the source, medium, and campaign details of website traffic. If these parameters are not properly included or are formatted incorrectly in URLs, GA4 cannot accurately identify the traffic source, leading to it being misclassified as direct.
Redirects Without Referrer Data
Redirects without referrer data is actually quite a large problem with any different causes behind it. Essentially, when a user clicks a link that leads to your website, the browser will send a “referrer” header to the destination site. This helps to indicate where the traffic came from. But in this case, various types of redirects can cause this referrer information to be lost which then leads GA4 to categorize the session as direct traffic.
There are four types of redirects that do this they are:
- 1. Meta Refresh Redirects
- 2. JavaScript-Based Redirects
- 3. URL Shorteners
- 4. Excessive Redirect Chains
In the next few paragraphs we are going to break down what each of these things mean and how they affect your direct website traffic.
1. Meta Refresh Redirects
First we have meta refresh redirects. As the name implies, they are involved in refreshing the page. These HTML tags will automatically refresh a page after a specified time interval. When this happens you will lose valuable data as they often do not pass referrer information. This then causes GA4 to misattribute the website traffic as direct.
2. JavaScript-Based Redirects
Depending on the setup of your website and your code you could be impacted by JavaScript redirects, such as window.location or window.location.replace, because they strip referrer data. A web browser may not pass referrer information when navigating via JavaScript leading to direct traffic attribution in GA4.
3. URL Shorteners
A URL shorter makes it easier to share links on platforms with character limits like social media. The URL shorters also make links easier to remember and type.
Sadly URL shorteners like Bit.ly for example can result in the loss of referrer data. When a user clicks on a shortened link, the referrer information may not be passed along, causing GA4 to register the session as direct traffic.
4. Excessive Redirect Chains
Excessive redirects are not only bad for SEO but they are also terrible for your analytics tracking. Multiple redirects between different domains can strip out referrer information. With every redirect you are introducing the possibility of losing the original referrer, leading GA4 to misclassify the session as direct traffic.
2. Dark Social and Messaging Apps
Dark social refers to social shares that can not be properly attributed. Normally, these are links that are being shared inside of Facebook messenger, WhatsApp, via email or Skype.
Given the fact social media is widely adopted this makes attribution and tracking difficult even for the most advanced marketers. Dark social can be considered similar to traditional word-of-mouth marketing but done online; elusive but highly rewarding.
As a marketer you should be willing to account for dark social. although there is little you can do to track its effectiveness.
3. Browser Privacy Settings
User privacy is increasingly important. People do not want to be tracked for every action they take hence the enhanced privacy settings and the rise of people using alternative browsers such as Brave, DuckDuckGo or at the very least Google’s Incognito mode.
Cookies are how Google tracks behavior with websites and apps. A browsers privacy settings can significantly impact how Google Analytics (GA4) classifies traffic when users have enabled privacy features like “Do Not Track” or other privacy extensions like ad blockers their browser may not transmit the necessary referrer information this is another cause for GA4 to attribute that traffic as direct.
Cookie Consent Solutions
In the exact same breath as a browser’s privacy setting is Cookie Consent. This helps to tell Google how to handle the tracking of a session from a given website. Delaying cookie consent can lead to lost session source data because Google Analytics relies on third-party cookies to track user behavior across different websites.
As a user delays or denies consent, Google Analytics may not be able to accurately identify the source of their traffic. and If they cannot classify the traffic they will simply attribute it to “Direct”.
Pages Missing GA4 Tracking Code
Sometimes issues with direct traffic in GA4 have nothing to do with redirects, missing UTM parameters or browser privacy settings. You may have an issue with untracked pages. When Google encounters a webpage that does not contain the Google Analytics tracking code it will mark that traffic as a “direct traffic” source by default.
Affiliate Links Without UTM Parameters
Affiliate traffic can be misclassified as direct traffic in Google Analytics when UTM parameters are missing from affiliate links. Without UTM parameters, Google Analytics cannot identify the source, medium, and campaign of the traffic, leading the system to categorize the traffic under “Direct” or “Unassigned”. This misclassification can obscure valuable data about the effectiveness of affiliate marketing efforts.
7. Strategies to Mitigate Direct Traffic Misattribution
1. Implement Consistent UTM Tagging
If you are going to market your business and use data to make data-driven decisions with analytics you should have standards. The best way to do this is to implement consistent UTM tagging practices.
There are two main things you’ll need to do to make this happen:
- Define Naming Conventions
- Standardize Your Approach
1. Define Naming Conventions
- Campaign: Create a consistent naming structure (e.g., “summer-sale-2025”). Consider using a date prefix or suffix to identify campaign periods.
- Source: Use the name of the platform or channel where the traffic originated (e.g., “facebook”, “google”, “email”, “twitter”).
- Medium: Specify the type of link used (e.g., “cpc”, “display”, “email”, “social”).
- Term: Use keywords for search campaigns or ad variations (e.g., “keyword-1”, “keyword-2”).
- Content: Distinguish between different call-to-action buttons or ad versions (e.g., “button1”, “headline1”).
2. Standardize Your Approach
- Lowercase and Underscores: Enforce lowercase letters and use underscores to separate words in your UTM parameters.
- Be Consistent: Apply your naming conventions consistently across all campaigns and platforms.
- Consider a Template: Create a template for generating UTM codes to ensure consistency.
Example
- Campaign Name: “summer-sale-2025”
- Source: “facebook”
- Medium: “cpc”
- Term: “discount-code”
- Content: “button1”
Putting It All Together
The final URL should look something like this.
https://www.example.com/?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=summer-sale-2025&utm_term=discount-code&utm_content=button1
Google has a great tool for this you can use here
2. Ensure Proper Redirects
Proper redirects are perfectly fine for SEO unless you do it incorrectly. If you decide to use 301 redirects you should take additional steps to persevere your referrer data. If you use too many redirects you may get confused. You should look to keep these to a minimum and only use them when you need them.
3. Optimize Cookie Consent Mechanisms
Given the strong push towards data privacy, cookie consent is not something you will be able to get around. To “optimize” cookie consent you should display the message as fast as possible and in a prominent location. The faster you get consent for analytics tracking the faster you will be able to collect the data you need.
4. Comprehensive GA4 Tracking Implementation
To avoid your website traffic being logged as direct ensure that you have property tagged every webpage. This will also help to maximize the amount of data you receive into your account leading to a higher ROI over time.
5. Monitor and Adjust for Dark Social
Monitoring for Dark Social is tricky but it can be done. The two best ways to do this are to use URL shorters and UTM codes. This will help you see more about what types of content is getting shared on social media and allow you to make additional enhancements to it on an as needed basis.
6. Utilize Server-Side Tagging
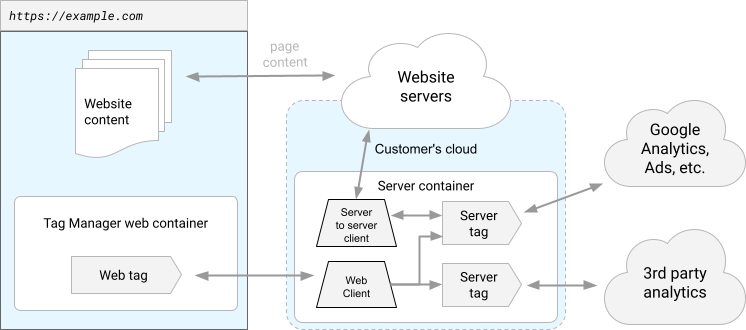
Adding Google Analytics to your website is not the only way to track users who are on your website or app. You can use server side tagging to cut down on the amount of direct traffic. If you want to use server side tagging you will need to use the Google Tag Manager. server side tagging is an advanced method and should be undertaken by a professional to ensure correct implementation.
7. Regular Audits and Testing
As a best practice you should always regularly review your marketing data with routine audits in order to identify and stop any misattribution issues you may have. By doing this you will also be able to stay on top of new trends with your overall website traffic and will be able to capitalize on the traffic that is coming to your website .
Conclusion
Now that you understand what direct traffic means in Google Analytics, and you understand how to combat its ability tio skew your data we encourage you to audit your GA4 setup to implement some of the stragies we laid out. If you need help from our team to get this done consider reaching out to a us.
We also recommend reading:
Evaluating Page Speed With Technical SEO
What Event Count Mean In Google Analytics
Does Using Other Pages’ Images in Your Website Hurt SEO?
Google Search Console Vs Rapid URL Indexer
How To Attract More Visitors To Your Google Business Profile
